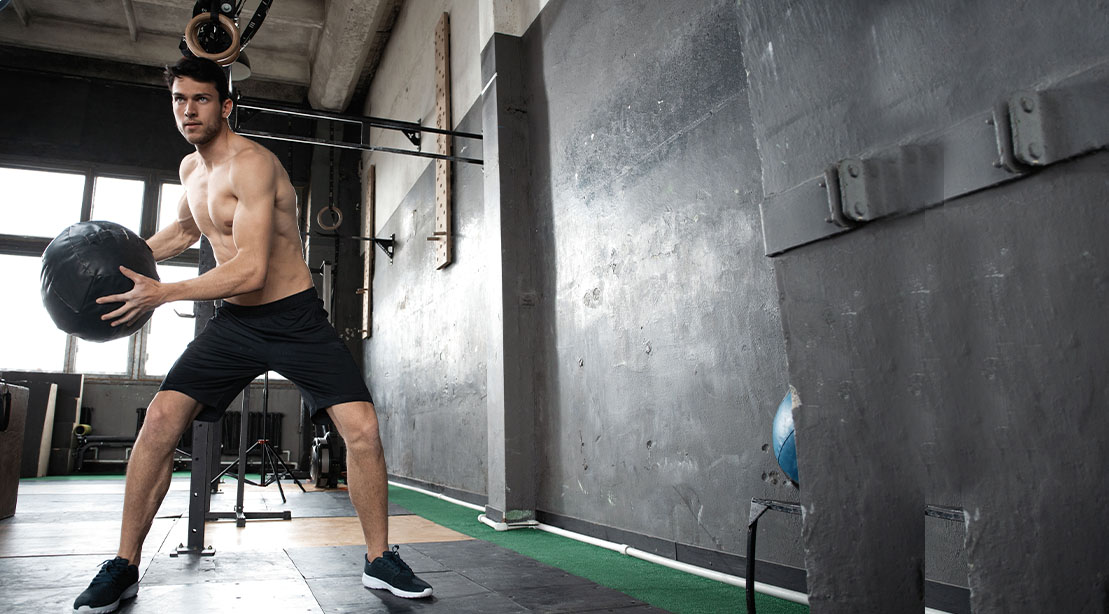
Med Ball Rotational Throws

You Want to be Powerful, Right?
You want to be powerful, right? Not just the kind that looks awesome but the type that transfers to daily movements—whether you’re on the field, in the gym, or leaping a building with a single bound. That’s where the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw comes in. It’s not about throwing a ball against the wall just for fun. This exercise improves rotational strength, core stability, and overall athletic power in one package.
What is the Med Ball Rotational Side?
At its core (pun intended), the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw is all about explosive power. You are twisting and throwing a med ball against the wall as fast and hard as possible. It’s a movement that teaches you how to generate force from the ground up, using your lower body to drive power through your hips and core into your upper body. But here’s the thing: your upper body is an extension of your hips. The magic happens in your hips and core because the power comes from your glutes and obliques. Your arms? They’re just along for the ride.
How to Perform The Med Ball Rotational Side Throw
- Stand 2 to 4 feet side-on to a wall, holding a med ball in both hands. Start with your feet about shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, and the ball resting on your back hip
- Start by slightly rotating your hips and shoulders toward the back leg, loading your back hip.
- From the back hip, quickly transfer your weight from the back leg to the front leg while explosively rotating your back foot, hips, and torso.
- As you rotate your torso forward, release the med ball, throwing it hard against the wall. Ensure you follow through with your arms for maximum power.
- Catch the ball on the rebound, return it to your back hip, and reset and repeat.
The Med Ball Rotational Side Throw Muscles Worked
Lower Body
Glutes: The glutes power the throw, especially during the weight transfer from back to the front leg via hip rotation and hip extension.
Adductors: Your inner thighs help stabilize and control the rotation.
Hip Internal and External Rotators: These muscles perform double duty, keeping your hips aligned throughout the rotation.
Core
Rectus Abs and Obliques: These muscles allow you to rotate and stabilize your torso while throwing. They both act as the bridge between your lower and upper body as they will enable the transfer of force without energy leaks.
Transverse Abdominis: Deep core muscles that protect your spine and assist with stabilizing it.
Upper Body
Shoulders (Deltoids): They guide the ball and power some of the movement via shoulder flexion
Forearms and Chest: These come into play when catching and resetting the ball for the next rep.
Benefits of The Med Ball Rotational Side Throw
Why should you add this exercise besides having a better-looking midsection? Well studies have shown a correlation to throwing velocity and may be a predictor of bat speed and exit velocity. Its benefits also include better performance, a stronger core, and injury prevention.
Enhanced Rotational Power:
Rotational power is essential for swinging a bat, throwing a punch, or improving athleticism. The med ball throw teaches your body how to create and transfer force effectively from the lower body to the upper body.
Full-Body Power:
Don’t underestimate how much your entire body works during this exercise. It works everything from head to toe, from your hips to your core, stabilizing your torso and arms and then throwing the ball against the wall.
Core Stability:
Sure, throwing a med ball against a wall is fun, but the real benefit here is how it strengthens your core’s ability to resist unwanted rotational forces. By focusing on power and control, you’re building bulletproof abs that can handle anything.
Injury Prevention:
Rotational exercises like this one protect your spine and hips from unnecessary strain during explosive movements. Training your body to control rotation lowers your risk of injury in workouts and daily life.
Common Med Ball Rotational Side Throw Mistakes and Fixes
Overusing the Arms:
Relying too much on your arms to power the throw is a big no-no. Remember, this is a hip-driven movement, and the arms are just along for the ride. To fix this, focus on initiating the movement from your hips and core. Please focus on the back hip and feet rotating towards where you are throwing it. If your back hip and foot are not facing the wall at the end of the movement, you’re using too much of your upper body.
Incorrect Ball Placement:
If you don’t start with the med ball on your back hip, you’re already limiting your power potential. The ball should always begin at your back hip, not in front of your body. This allows for a total weight transfer from the back leg to the front, generating maximum force with each throw. Keep the ball low and close to the body as you wind up and throw.
Incorrect Feet Placement:
Your feet are the foundation of this movement, and you will lose power if your stance is not wide enough. Ensure your feet are shoulder-width apart and you’re transferring your weight smoothly from the back to the front foot during the throw. A stable base equals more power and control.
Conclusion
The Med Ball Rotational Side Throw is a powerful exercise that targets your entire body, improving rotational strength, core stability, and overall athletic power. By incorporating this exercise into your routine, you’ll be able to unleash your full potential and achieve the results you desire. So, get ready to unleash your inner athlete and start throwing like a pro!
FAQs
Q: What is the main muscle group worked during the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw?
A: The main muscle group worked during the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw is the glutes, along with the adductors, hip internal and external rotators, core, and upper body muscles.
Q: What are the benefits of the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw?
A: The benefits of the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw include enhanced rotational power, full-body power, core stability, and injury prevention.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid during the Med Ball Rotational Side Throw?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include overusing the arms, incorrect ball placement, and incorrect feet placement. By focusing on proper form and technique, you can ensure you get the most out of this exercise.